
Letter 2 – Chamber sensed: chamber where intrinsic depolarization is detected Letter 1 – Chamber paced: chamber where pacemakers leads are located For patients in the ED, it is important to focus on the first three letters:
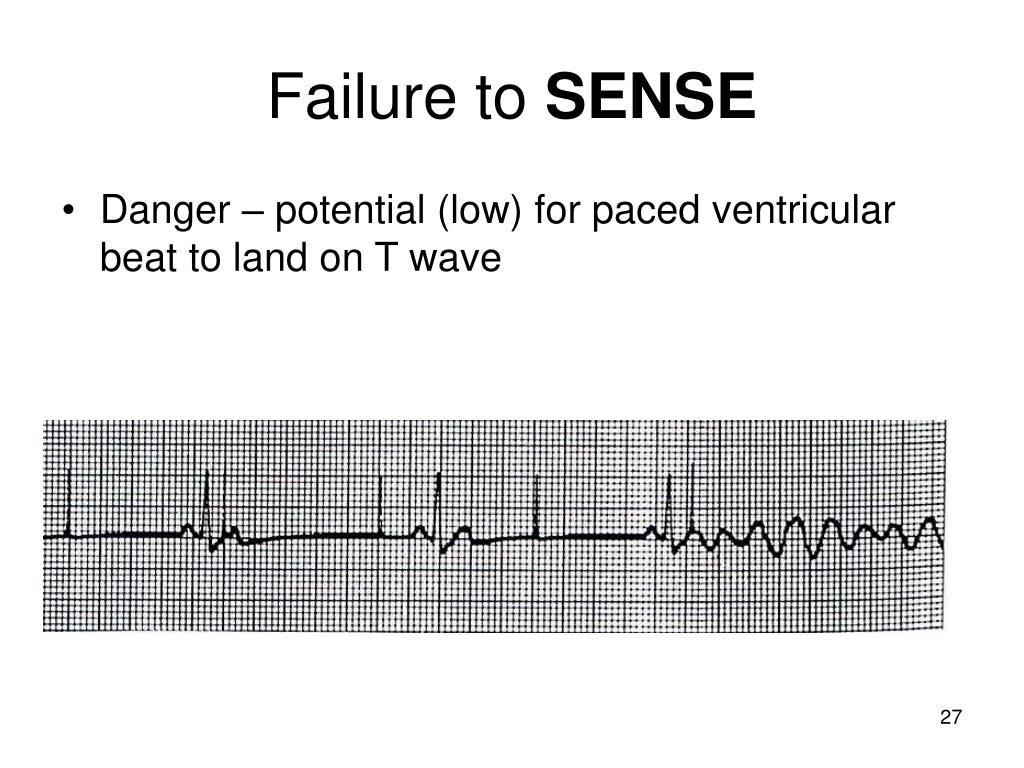
#FAILURE TO CAPTURE PACER SPIKES CODE#
The North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology/British Pacing and Electrophysiology Group (NASPE/BPEG) Pacemaker code is a five-letter series that describes the settings of a patient’s pacemaker. How do we interpret this ECG? What are the significant findings that can discern information about the type of pacemaker placed?īefore discussing the ECG above, it is important to understand the basics of interpreting the ECG of a patient with a pacemaker. For patients with refractory Afib and reduced systolic function, the nodal ablation and pacemaker approach showed small but statistically significant improvement in echocardiographic parameters as well.įollowing placement of the pacemaker, the following ECG was obtained. One meta-analysis comparing AV-nodal ablation with pacemaker to pharmacologic therapy alone for refractory afib found that AV-nodal ablation/pacemaker led to a significant improvement in quality of life and symptoms with minimal morbidity. The European Society of Cardiology guidelines are similar but suggest first considering direct catheter-based or surgical ablation to eliminate the abnormally firing impulses in the atrium. According to American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association/Heart Rhythm Society guidelines, this is a reasonable approach when pharmacological therapy is inadequate and rhythm control cannot be achieved. Doing so, however, necessitates a pacemaker to generate a heart rate to provide appropriate cardiac output. By ablating the AV node and blocking impulse conduction through it, the misfiring atrium is ignored. Ultimately, the patient underwent AV node ablation and dual chamber permanent pacemaker placement. Cardioversion was contraindicated as TEE demonstrated evidence of thrombosis in the left atrial appendage. The Afib with RVR remained uncontrolled despite high doses of esmolol and metoprolol.
The patient was transferred to the CCU and started on an esmolol drip and metoprolol.
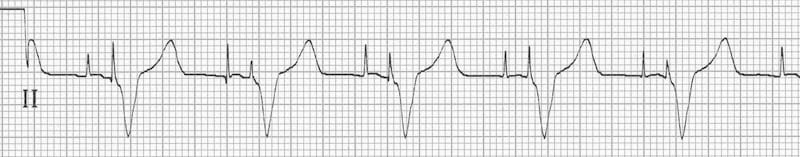
However, over the course of one week, her Afib with RVR recurred and persisted with rates 130s-160s, not responding to nasogastric or IV medication. Initially, rate control was attempted with metoprolol via nasogastric tube. During the inpatient admission, the patient developed new-onset atrial fibrillation (Afib) with rapid ventricular response (RVR) (ECG below). Peer Editors: Alec Feuerbach and Nicole AnthonyĪ 72-year-old female with a past medical history of hypertension, hyperlipidemia, asthma, CVA with residual right sided weakness and aphasia was admitted to the hospital from subacute rehabilitation after a recent subacute infarct.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
